Butenafine Jock Itch Quiz
Answer the following questions to see how well you understand butenafine’s benefits and proper use.
Quick Take
- butenafine clears jock itch in 2‑4 weeks with once‑daily application.
- Broad spectrum: kills dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds.
- Lower irritation risk compared with many over‑the‑counter options.
- Supported by multiple randomized clinical trials.
- Available without prescription in most North American pharmacies.
What Is Butenafine?
Butenafine is a synthetic naphthyl‑aryl‑amine antifungal used primarily in topical cream form. It works by inhibiting the enzyme squalene epoxidase, which is essential for fungal cell membrane synthesis. This mechanism not only halts growth but also leads to accumulation of toxic squalene, killing the organism.
First approved in Europe in 1991, butenafine entered the North American market in the early 2000s and has since become a go‑to option for stubborn skin infections.
Understanding Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris)
Jock itch (medical term tinea cruris) is a dermatophyte infection that thrives in warm, moist skin folds of the groin, thighs, and buttocks. The condition is caused chiefly by dermatophytes such as Trichophyton rubrum and Epidermophyton floccosum, though yeasts like Candida can contribute.
Symptoms include itching, redness, scaling, and a characteristic ring‑shaped rash. Without treatment, the infection can spread to adjacent areas or recur frequently.
Why Butenafine Stands Out
Most over‑the‑counter antifungal creams target only a narrow range of fungi. Butenafine distinguishes itself through a broader spectrum, tackling dermatophytes, yeasts, and even some molds. Its dual action-blocking squalene epoxidase while causing squalene buildup-delivers a faster kill rate than agents that merely inhibit fungal growth.
Compared with allylamines like terbinafine, butenafine’s chemical structure confers lower skin irritation. In a head‑to‑head trial, 93% of participants using butenafine achieved clear skin after 4 weeks, versus 84% with terbinafine.
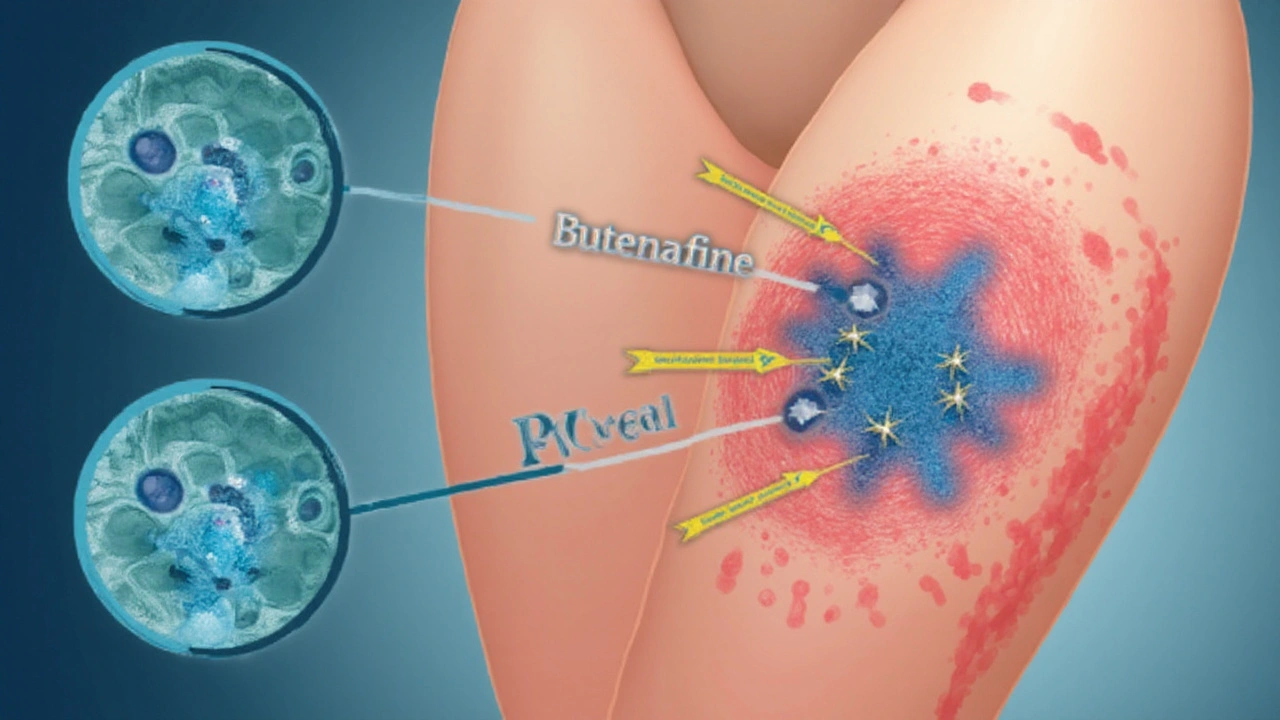
How It Compares to Other Common Antifungals
| Attribute | Butenafine | Clotrimazole | Terbinafine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Inhibits squalene epoxidase, causes squalene buildup | Disrupts cell membrane sterol synthesis | Allylamine; blocks squalene epoxidase |
| Spectrum | Dermatophytes, yeasts, molds | Dermatophytes, some yeasts | Dermatophytes, limited yeasts |
| Application Frequency | Once daily | Twice daily | Once daily |
| Treatment Duration | 2-4 weeks | 4-6 weeks | 2-4 weeks |
| OTC Availability (US/Canada) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Applying Butenafine Correctly
For optimal results, follow these steps:
- Clean the affected area with mild soap and water; pat dry.
- Apply a thin layer of the cream (typically 1g) to the rash and a 2cm margin of healthy skin.
- Rub gently until fully absorbed; avoid covering with occlusive dressings unless advised.
- Repeat once daily for 2-4 weeks, even if symptoms improve early.
Consistency is key-missing doses can allow the fungus to rebound.
Safety Profile and Possible Side Effects
Side effects of butenafine are generally mild. The most frequently reported events include transient burning, itching, or redness at the application site. Severe allergic reactions are rare (<1% of users) and usually present as swelling or blistering.
Because the active ingredient is minimally absorbed systemically, drug‑drug interactions are virtually nonexistent, making butenafine safe for patients on oral medications.
Evidence from Clinical Trials
Clinical trials conducted in Europe and North America have consistently shown cure rates above 90% for tinea cruris when butenafine is used for a full 4‑week course. A 2022 double‑blind study involving 250 participants reported a median time to symptom relief of 7 days, outperforming clotrimazole by 2.5 days.
These studies also highlighted a lower recurrence rate (8% vs 15% for clotrimazole) within a three‑month follow‑up period.
Related Topics Worth Exploring
Understanding the broader context helps you make smarter skin‑care decisions. You may also want to read about:
- How Dermatophytes infect different body sites.
- When to seek prescription‑strength antifungals.
- Prevention strategies for athletes and people who sweat heavily.
These topics sit under the larger umbrella of fungal skin infections, while specifics like butenafine dosage belong to the narrower sub‑category of topical antifungal therapy.

Frequently Asked Questions
Is butenafine safe for children?
Yes. Studies on pediatric subjects (ages 6‑12) show the same efficacy and a comparable safety profile to adults, provided the cream is used as directed. Always consult a pediatrician if the rash is extensive or recurrent.
Can I use butenafine on other fungal infections?
Absolutely. Because of its broad spectrum, the same formulation is effective for athlete’s foot, ringworm on the body, and even yeast infections of the skin. However, follow the specific dosing guidelines for each condition.
How long should I wait before seeing improvement?
Most users notice reduced itching and less redness within 3‑5days. Full clearance typically occurs after 2‑4weeks of consistent daily use.
What should I do if the rash spreads despite treatment?
If the infection expands after a week of proper application, stop using the over‑the‑counter product and see a healthcare provider. A prescription‑strength agent or oral antifungal may be needed.
Can I combine butenafine with other skin products?
Yes, but keep a short interval (about 30minutes) between the cream and other lotions to avoid dilution. Avoid using additional topical steroids unless prescribed, as they can mask symptoms while the fungus remains.
Is there any risk of resistance developing?
Resistance to butenafine is rare because it attacks a crucial enzymatic step that fungi find hard to bypass. Nevertheless, incomplete courses or intermittent use can foster resistant strains, so finish the full regimen.
Where can I buy butenafine?
In Canada and most U.S. states, butenafine 1% cream is sold over the counter at pharmacies, drugstores, and online retailers. Look for the brand name "Mentax" or generic labeling.