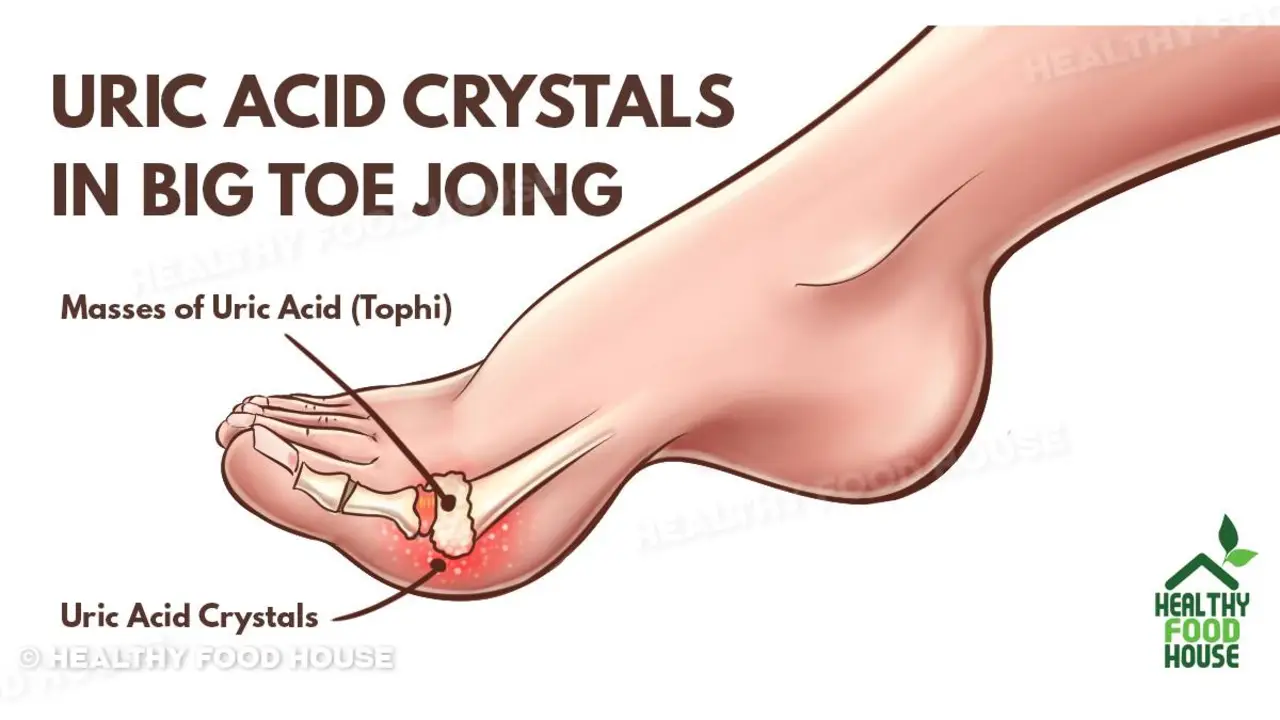
Think gout only hits people who eat steak and drink champagne? That's a common story, but it's misleading. Gout is an inflammatory arthritis caused by uric acid crystals in the joint. Diet plays a role, but genetics, kidney function, body weight and some medicines matter more than most think.
Myth: Only rich people get gout. Fact: Gout can affect anyone. Processed food, obesity and common medications raise risk, not just fancy meals.
Myth: All alcohol is equally bad. Fact: Beer raises gout risk more than wine. Beer contains yeast and purines that boost uric acid. Red wine in moderation is less risky, but binge drinking is still harmful.
Myth: Dairy makes gout worse. Fact: Low‑fat dairy often lowers uric acid and can reduce flare risk. Plain yogurt and skim milk are generally safe choices.
Myth: You can cure gout with diet alone. Fact: Diet helps but usually won't stop flares if uric acid stays high. Many patients need urate‑lowering medicine like allopurinol or febuxostat to reach target uric acid and prevent attacks.
Myth: Normal blood uric acid rules out gout. Fact: Uric acid can be normal during or between attacks. Diagnosis depends on symptoms and sometimes joint fluid analysis to see crystals.
Keep hydrated. Drinking water helps kidneys clear uric acid. Aim for steady, regular fluids rather than chugging once a day.
Cut sugary drinks and limit beer. Fructose‑sweetened sodas and beer are two of the biggest dietary triggers. Replace soda with water, sparkling water, or unsweetened tea.
Watch portion sizes of high‑purine foods. You don’t have to avoid meat and seafood entirely—use moderation. Try more beans, vegetables, and whole grains.
Talk to your doctor about urate‑lowering therapy. If you get repeated flares or have uric acid above the recommended target, medicines like allopurinol lower uric acid long term and reduce attacks. Starting treatment is often the turning point.
Use fast treatment for flares. At the first sign of a flare, short courses of NSAIDs, colchicine, or a steroid usually shorten the attack. Don’t wait for it to peak—treat early.
Monitor other conditions. High blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease interact with gout. Managing these makes gout care simpler and safer.
When to see a specialist: if attacks are frequent, if joints look damaged, or if you have kidney stones. A rheumatologist can tailor treatment and adjust medications safely.
Gout isn't a moral failing or a simple food problem. Understand the real drivers, use proven treatments, and you can get control—often with fewer flares and less pain.
Keep track of your uric acid numbers and medication side effects. A simple log helps when you talk with your doctor. Don’t stop urate‑lowering drugs during a flare unless your clinician tells you to; stopping can actually trigger more problems. Small steady weight loss (5 to 10% of body weight) often lowers uric acid and cuts attack frequency. Combine exercise you enjoy with changes to your eating
Hi there, gentlemen! In today's blog post, we're going to tackle some of the most common myths and misconceptions surrounding high uric acid levels and gout. I bet you've heard many of them before, but rest assured, our aim is to debunk these myths and arm you with the facts. Let's navigate this journey together, separating fact from fiction when it comes to your health.
What transit actually does to cut gridlock. Clear mechanisms, real numbers, case studies, and a step-by-step playbook cities can use in 2025.
Sudden shortness of breath could be a sign of pulmonary embolism - a life-threatening blood clot in the lungs. Learn the key symptoms, how doctors diagnose it, and why acting fast saves lives.
I recently discovered the incredible benefits of Scurvy Grass, a dietary supplement that's truly a game changer. Packed with essential nutrients like vitamin C, iron, and calcium, it's a powerhouse for immune support and overall health. Not only does it help prevent scurvy, but it also aids in digestion, supports bone health, and has anti-inflammatory properties. I've been incorporating it into my daily routine, and I'm already noticing a difference in my well-being. If you're looking for an all-natural supplement to boost your health, I highly recommend giving Scurvy Grass a try!
Learn how OnlinePillsWWW.com is changing the way people buy prescription drugs online. Get tips for safety, legal info, and how to spot legit pharmacies.
Combining metformin and alcohol can trigger lactic acidosis-a rare but deadly condition. Learn the real risks, symptoms to watch for, and what experts actually recommend for people with type 2 diabetes who drink.